Cybersecurity Awareness Month - October 2023
It's easy to stay safe online.
2023 marks 20 years of Cybersecurity Awareness Month!
This year’s theme is “It's easy to stay safe online.” The theme aims to make actionable steps positive, approachable, and back-to-basics to help people protect themselves from cyber criminals. It reminds internet users that there are plenty of simple ways to stay secure when online. -Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA)/National Cybersecurity Alliance (NCA)
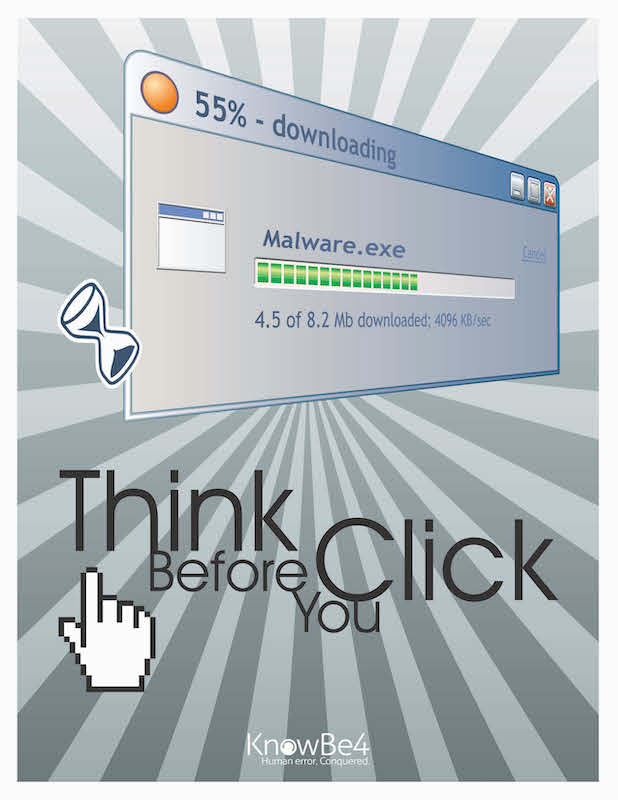
Cyber threats can be scary, and for good reason. Malware can be lurking in a suspicious email or text and all it takes is a click or a download for a breach to occur and cause severe damage to an organization. During Cybersecurity Awareness Month, we will share best practices and tips to help us stay cyber-safe everywhere we go. We will learn how simple and practical steps can prevent cyber attacks from being successful.
This year’s campaign will focus on the following four key practices that are simple and actionable for both individuals and businesses.
- Week 1: Security culture and you
- Week 2: Enable multi-factor authentication
- Week 3: Recognize and report phishing
- Week 4: Keep software updated
Events
National Cybersecurity Alliance (NEIU participants will be joining other Illinois universities).
-
Behavioral science presentations:
-
Friday, Oct. 6 at 1:00 p.m. EST (noon CT). Sign-up is required.
-
Tuesday, Oct. 24 at 5:00 p.m. EST (4:00 p.m. CT). Sign-up is required.
-
Game show: Tuesday, Oct. 10 at noon EST (11:00 a.m. CT). Sign-up is required.
In-person sessions and a trivia night hosted by the Computer Science Department.
-
Women in Cybersecurity Panel discussion: Tuesday, Oct. 10 from 3:00-4:00 p.m. in Room CBT 149
-
Cybersecurity information session - cybersecurity career paths (NEIU degree programs and certifications in cybersecurity): Thursday, Oct. 19 from 3:00-4:00 p.m. in Room LWH 1001
-
Fall trivia night: Monday, Oct. 30 from 4:30-5:30 p.m.
* The Computer Science Department has provided additional resources for Cybersecurity Awareness Month. To learn more, please visit the Computer Science Department.
Thanks, and have a cyber-safe October!
WEEK ONE: Security culture and you
An organization's security strength and resilience depend on the culture that drives it. - UTS
Statistics:
- Nearly 90% of all data breaches happen because of poor cybersecurity posture (Balbix).
- 79% of consumers polled said organizations have an obligation to take reasonable steps to secure their personal information (Computer Weekly).
- Human error is the main cause of 95% of cybersecurity breaches (IBM).
focus
This week's focus: What is a security culture and how can you contribute to it?
Security culture is defined as the ideas, customs, and social behaviors of a group that influence its security. By helping to create a strong security culture, we can protect our organizations and homes from cyberattacks. (Knowbe4)
A strong security culture promotes principles and practices to protect a community from events that could compromise its critical resources and operations. It requires partnership and ownership across all members of that community to engage in these practices.
My role: Information security is a shared responsibility and I can be proactive in cultivating a culture of good practices by knowing what to do and caring enough to do it.
An organization’s employees are at the center of everything; they can either be easy prey, or they can become an effective human layer of defense (Knowbe4). Remember, it's easy to stay safe online when we embrace a good security culture.
The videos below provide more insight into what an information security culture is with a few examples of good security practices such as securing passwords and how to prevent being phished.
Training videos (Please click on the Library tab):
- Security Culture and You (4 minutes)
- Eight Ways to Strengthen and Secure Your Passwords Today (5 minutes)
- Mobile-First Module: Phishing: Don’t Get Reeled In (4 minutes)
Game: Cybersecurity Trivia Twirl (external link)
Posters:
WEEK two: Enable multi-factor authentication
Wouldn't it be nice to provide the best security for the things that are valuable to you so you worry less about their safety? Multi-factor authentication enables individuals and organizations to protect their user accounts so they worry less about the safety of the information held in the accounts. - UTS
Statistics:
- According to Microsoft, multi-factor authentication prevents 99.9% of automated assaults on its platforms’ websites and other online services.
- 99.9% of hacked accounts did not use MFA (Microsoft).
- Google’s data showed that having a text message sent to a person’s phone for additional verification prevented 100% of automated bot attacks that use stolen passwords and 96% of phishing attacks that try to steal passwords.
focus
This week's focus: Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA)
The use of multi-factor (MFA) or two-factor authentication continues to grow as security trends show that MFA plays a key part in reducing data breaches resulting from compromised user accounts.
In addition to a username and password, MFA enforces verification from a user logging into an account to prove their identity in multiple ways before the user can access the account. The additional verification method is registered to the owner of the account and only the owner can provide the verification. Additional verification methods may include:
- A push notification to an MFA mobile app which the owner can approve or decline.
- Randomly generated PIN codes on an MFA mobile app or from an MFA hardware device.
- A call or a text message to receive a PIN code.
- Fingerprint, palm scan, face ID, or voice recognition.
Almost all service providers offer MFA and it is important to enroll to use MFA if it is available. The more user accounts you enable MFA on, the safer your information is and the less worried you can be about changing your password frequently unless you believe it is compromised. Examples of services that offer MFA are:
- Financial services
- Social media
- Online retail stores
- Email services
- Internal Revenue Service (IRS)
- Credit monitoring services
- Airlines
My role: I can protect myself and my organization by using and managing my user accounts securely.
Remember, it's easy to stay safe online when we take responsibility for information security. Below are some simple but practical steps that can help keep our user accounts secure:
- Don't delay to use MFA if it is available. Learn more about the University's MFA tool.
- MFA still requires the use of passwords or passphrases. Use strong passwords and don't share them. The longer your password, the more difficult it is for hackers to crack. Change it at least once every six months if MFA is enabled.
- Keep your devices locked when not in use and stored away in your absence. MFA will not protect your user account or information if you leave your computer unlocked and unattended.
- Watch out for phishing attacks. Stop, look, and think before you respond to unsolicited or suspicious emails, texts, or calls.
- Watch out for MFA hacking. Don't approve any MFA push notification that you did not request or share your MFA PIN with anyone.
- Visit our Cybersecurity Tips for more good practices.
Training videos: (Please click on the Library tab)
- KnowBe4 Pretexting - "Tech Support" Social Engineering (5 minutes)
- Multi-factor Authentication Attack (5 minutes)
- Danger Zone Interactive session (5 minutes)
Poster:
WEEK THREE: rECOGNIZE AND REPORT PHISHING
It is easier and cheaper to manipulate people using social engineering to gain access to information, IT systems, or buildings than to use technical tools. Why? People can easily be convinced to ignore simple security practices that are there to protect them if they believe they need to act immediately or show goodwill in response to a request. - UTS
...So you need to be able to recognize phishing so you don't fall for it!
Statistics:
- 91% of all attacks begin with a phishing email to an unsuspecting victim (Deloitte).
- Education was the most targeted industry in 2022 for phishing, with attacks increasing by 576% (Zscaler).
- Human error is the main cause of 95% of cybersecurity breaches (IBM).
focus
This week's focus: Recognize and report phishing
Phishing is a tactic used by cybercriminals to trick people into believing something to make them divulge sensitive information or click on a malicious link. This could then be used by cybercriminals to carry out harmful activities, including gaining unauthorized access to IT systems and information, impersonating individuals for financial gain, carrying out ransomware attacks, etc.
Phishing scams are becoming very sophisticated and almost believable if you don't know what to look for. They are usually carried out through emails, text messages, social media, and phone calls.
Most phishing attacks share common characteristics and often use familiarity or current issues to increase the likelihood of a victim falling for these scams. The goal is always to steal vital information or compromise IT systems which could then be used to carry out further attacks.
A good way to prevent being phished is to stop, look, and think to be sure before you respond.
Recognizing phishing:
- Who is the message coming from and can the sender be trusted? Look for misspellings in the email address, message, or the link provided. Watch out for email addresses or telephone numbers that you are not familiar with.
- Does it appear to be a random or unusual message even if the person/entity is known? Contact the person or entity directly using known contact information such as their telephone number or visit the organization's website.
- Is the message alarming and are you being asked to take urgent action like changing your password, downloading an attachment, or purchasing some gift cards? Check with the IT department or information security team for advice.
- Are you being asked for a favor because the sender or caller appears to be in need? Don't take any action that may compromise your or other people's information, or purchase items on behalf of someone.
- Are you being offered a service and asked or directed to provide information that may be sensitive such as your login details, MFA approval or pin code, social security number, etc? End the communication and contact the relevant organization from a known number.
- Watch out for freebies. If it is too good to be true, it probably is!
Blocking and reporting phishing:
It is important that you report phishing as soon as possible to stop it from spreading further. You should also block the sender from sending other emails to you. Different email platforms such as Outlook, Yahoo, Gmail, etc., have different ways of blocking and reporting phishing and you should check each platform on how to do so. In Gmail, follow the steps below:
- Select the three vertical dots in the phishing email as shown in the image below:
![]()
- Select from the options listed to either report spam, or report phishing.
- After reporting it, block the sender and delete the email.
My role: My responsibility is to protect the information that is valuable to me and the University by identifying phishing scams and responding to them appropriately.
Training Videos: (Please click on the Library tab)
- Phil Hendrie & Kevin Mitnick: Credential Harvesting Attack (5 minutes)
- Micro-module - Email Spoofing (4 minutes)
Game: Cybersecurity trivia twirl (external link)
By identifying phishing scams, responding to them appropriately, and reporting them promptly, we keep ourselves and the University safer. Remember, it's easy to stay safe online when we embrace a good security culture. See the posters to learn.
Posters:
WEEK FOUR: KEEP SOFTWARE UPDATED
THINK TWICE BEFORE PUTTING OFF UPDATES!
"Many people might select “Remind me later” when they see an update alert. However, many software updates are created to fix security risks. Keeping software up to date is an easy way for us to stay safer online." - CISA
Statistics:
- Over 8,000 vulnerabilities were published in Q1 of 2022 (Comparitech).
- According to Unit 42, 48% of ransomware cases began with software vulnerabilities (Palo Alto).
- 57% of cyberattack victims said their breach was due to unpatched vulnerabilities, and 34% knew of the vulnerability but failed to apply patches in time (Cyrebro.io).
focus
This week's focus: Keep Software Updated
Software solutions are designed to facilitate processes so that we can carry out daily activities efficiently. Software providers have the responsibility of identifying flaws in their solutions and providing fixes and updates to address these flaws to maintain software functionalities and security and to prevent opportunities that hackers could use to exploit their software.
Hackers are always looking for ways to exploit vulnerabilities (weaknesses) in software and the easiest way to achieve this is to look for software that is not updated with the relevant security patches. This means that every time a software update is delayed or ignored, it creates an opportunity for a hacker to compromise the computer running that software. However, if we maintain the latest updates and fixes for the software we use, we not only benefit from using the latest features the software offers, but we also make our devices and information more secure.
My role: My responsibility is to keep the software on my devices up-to-date. Below are some basic steps to follow:
- Turn automatic updates on. This makes it easier for software to be downloaded and installed as soon as they are available without you having to check every time.
- Watch for software notifications. Your device will always notify you when there is a new update or your organization may ask you to update software used for work. Don't ignore the notification but act responsibly and update the software as soon as possible.
- Software and app downloads: Only download software directly from verified sources and app stores.
- Don't fall for app freebies. You may be downloading malware on your computer!
- Watch out for fake software fixes. If you receive an unusual email, text, call, or a pop-up window to fix your device or update your software, contact IT Helpdesk directly to check before you respond to it.
Training Videos: (Please click on the Library tab)
- Captain Awareness: Protect Your Web Browser (2 minutes)
- Micro-module - Introduction to Ransomware (5 minutes)
To keep our devices and information safer, we need to ensure the software we use is kept up-to-date. Remember, it's easy to stay safe online when we embrace a good security culture. See the poster to learn.
Poster:
Thank you for participating in this year's Cybersecurity Awareness Month.